Customizing a Mathfield
The appearance and behavior of the mathfield is highly customizable.
In this section we'll go over some of the ways a mathfield can be customized.
Styling
To style the mathfield define a CSS rule targeting the mathfield or use the
style attribute of the <math-field> element.
CSS attributes can be used to modify the appearance of the mathfield in many ways, for example changing the base font size or adding a border around it.
To remove the border around the mathfield, set the
border property to none or 0.
To change the background color of the mathfield, use the background property.
To display the mathfield as a block element, rather than an inline element,
add an attribute style="display: block"
CSS Variables
To customize the appearance of the mathfield, use the following CSS variables (custom properties) in a ruleset that applies to the mathfield element.
math-field {
--smart-fence-color: red ;
}
Although CSS styles are "invisible" to custom components, CSS variables are
"passed through" and will affect the content of the <math-field> custom component.
Set these CSS variables on any selector that applies to the
<math-field> element you want to customize, for example, body.
Alternatively these CSS variables programatically can be set programmatically:
document.body.style.setProperty("--smart-fence-color", "red");
| CSS Variable | Usage |
|---|---|
--primary | Primary accent color, used for example keyboard toggle and menu glyphs and in the virtual keyboard |
--caret-color | Color of the insertion point |
--selection-color | Color of the content when selected |
--selection-background-color | Background color of the selection |
--contains-highlight-background-color | Background color of items that contain the caret |
--placeholder-color | Color of the placeholder symbol |
--placeholder-opacity | Opacity (0-1) of the placeholder symbol |
--smart-fence-color | Color of a smart fence (default is current color) |
--smart-fence-opacity | Opacity of a smart fence (default is 50%) |
--highlight-text | The background color indicating the caret is in a text zone |
--text-font-family | The font stack used for content in a text zone |
--latex-color | The color of content in a LaTeX zone |
--correct-color | Highlight color of a prompt when in the "correct" state |
--incorrect-color | Highlight color of a prompt when in the "incorrect" state |
For color values, you can use any valid CSS color value, such as a color name, or `transparent to remove the color.
Note To change the placeholder symbol, use the mf.placeholderSymbol property.
You can customize the appearance and zindex of the virtual keyboard panel with some CSS variables associated with a selector that applies to the virtual keyboard panel container.
Read more about customizing the virtual keyboard appearance
Mathfield Parts
Because the mathfield is a custom element with a shadow DOM, its content is not directly accessible to CSS rules outside of the shadow DOM.
However, there are a few parts that can be used to style the
content of the mathfield using the ::part() pseudo-element.
| Pseudo-element | Usage |
|---|---|
virtual-keyboard-toggle | The virtual keyboard toggle button |
menu-toggle | The menu toggle button |
content | The math formula |
container | The element containing the formula, the keyboard toggle and the menu toggle |
keyboard-sink | The hidden element capturing the physical keyboard input |
placeholder | The element containing the placeholder attribute when the mathfield is empty |
prompt | The prompts (placeholder{}) inside the mathfield |
For example:
/* Right align the formula */
math-field::part(content) {
text-align: right;
}
/* Right align the virtual keyboard toggle */
math-field::part(container) {
flex-flow: row-reverse;
}
/* Hide the virtual keyboard toggle */
math-field::part(virtual-keyboard-toggle) {
display: none;
}
/* Hide the menu toggle */
math-field::part(menu-toggle) {
display: none;
}
Note When the menu toggle is hidden, the menu can still be opened by right-clicking on the mathfield. You can customize the menu to change this behavior.
Placeholder
To customize the placeholder text set the placeholder attribute on the
<math-field> element.
Note that the content of the placeholder attributed is interpreted as a
LaTeX string. To display it as regular text, use the \text{} command.
Focus Ring
To change the appearance of the focus ring, use the :focus-within pseudo-element.
Caution Removing outlines in CSS creates issues for people navigating the web with a keyboard. However, you can change the appearance of the outline, for example to indicate an error condition. If you remove the outline on the mathfield, make sure to replace it with another indicator, for example by displaying an outline on an enclosing element.
Math Display Options
The appearance of a formula, in an editable mathfield or as a static representation, can be controlled with some of the following options:
Color
To change the foreground ("ink") and background ("paper") colors of a formula
programmatically, use the mf.applyStyle() function.
To change the foreground color, use the \textcolor{}{} command.
To change the background color, use the \colorbox{}{} command.
The first argument of these commands is a color specified as:
- a RGB color using the standard CSS format (
#d7170b) - a CSS color name (
goldenrod) - one of the 68 colors from dvips color name (
cadetblue) - one of the 10 Mathematica color from
ColorData[97, "ColorList"](m0tom9) - a color defined using the syntax from the
xcolorpackage, for example:blue!20!black!30!green
The following color names are recommended. They can be applied using the color keys in the virtual keyboard:
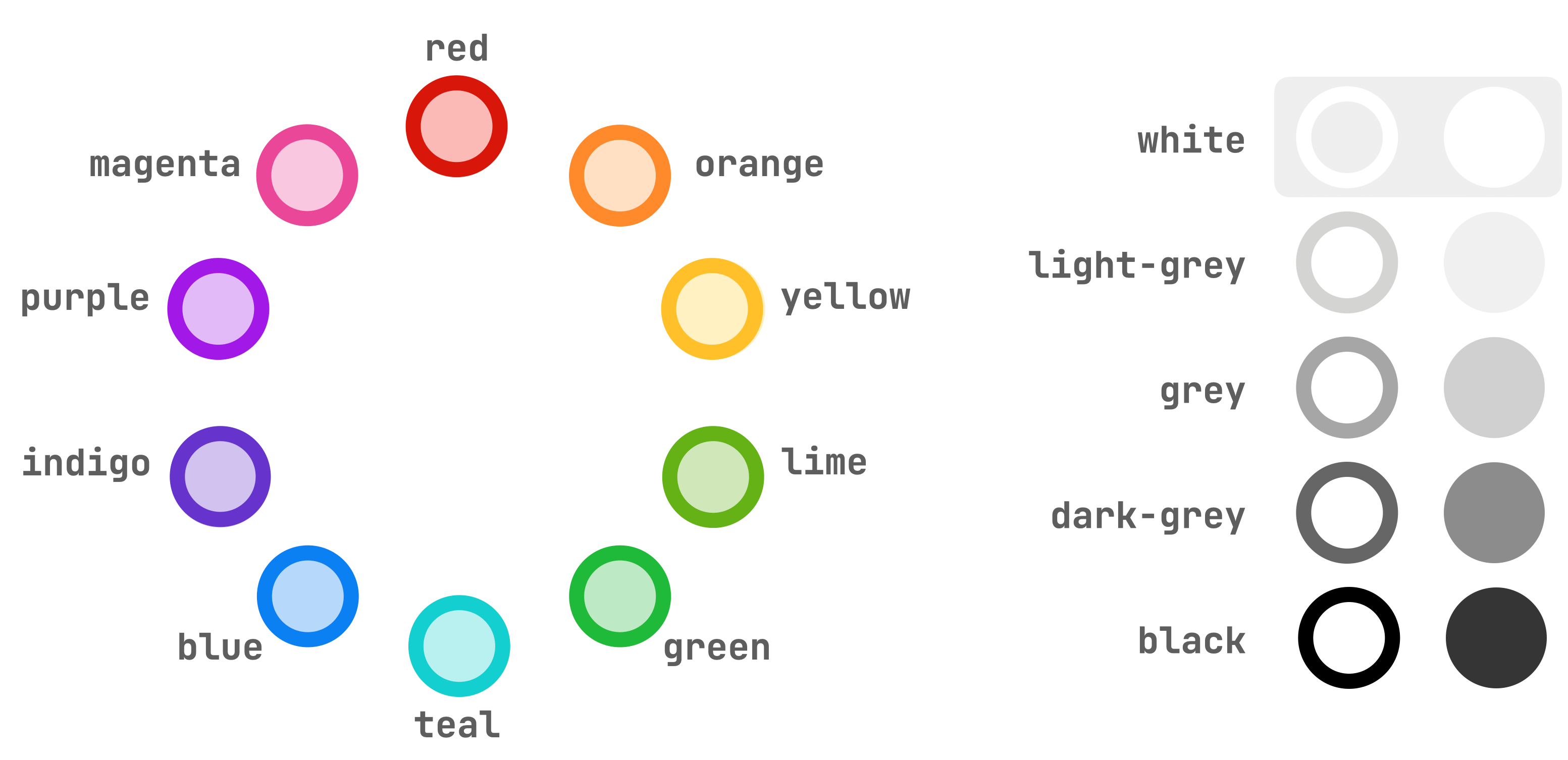
These colors have been carefully selected for a balanced representation of the range of
hues on the color circle, with similar lightness and intensity. They will map to different color values than the dvips colors of the same name.
To have proper legibility based on usage, these color names will map to different values when used as a foreground color and a background color. To use a specific color value, use a RGB color instead.
To customize how the color names are interpreted provide a colorMap
or backgroundColorMap function.
Size
To change the base font size, set the font-size CSS property to the desired
value on the mathfield or static element.
Within a formula, the size can be specified from a font scale with 10 values, where 1 em is the base font size of the mathfield or static element.
fontSize | LaTeX Command | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 em | \tiny |
| 2 | 0.7 em | \scriptsize |
| 3 | 0.8 em | \footnotesize |
| 4 | 0.9 em | \small |
| 5 | 1 em | \normalsize or \normal |
| 6 | 1.2 em | \large |
| 7 | 1.44 em | \Large |
| 8 | 1.728 em | \LARGE |
| 9 | 2.074 em | \huge |
| 10 | 2.488 em | \Huge |
In TeX, the sizing commands behave inconsistently when applied to math. Other implementations of TeX may also interpret the sizing commands differently.
Math Layout
To control some aspects of the math typesetting, change the mathstyle with
the commands \displaystyle, \textstyle, \scriptstyle, \scriptscriptstyle.
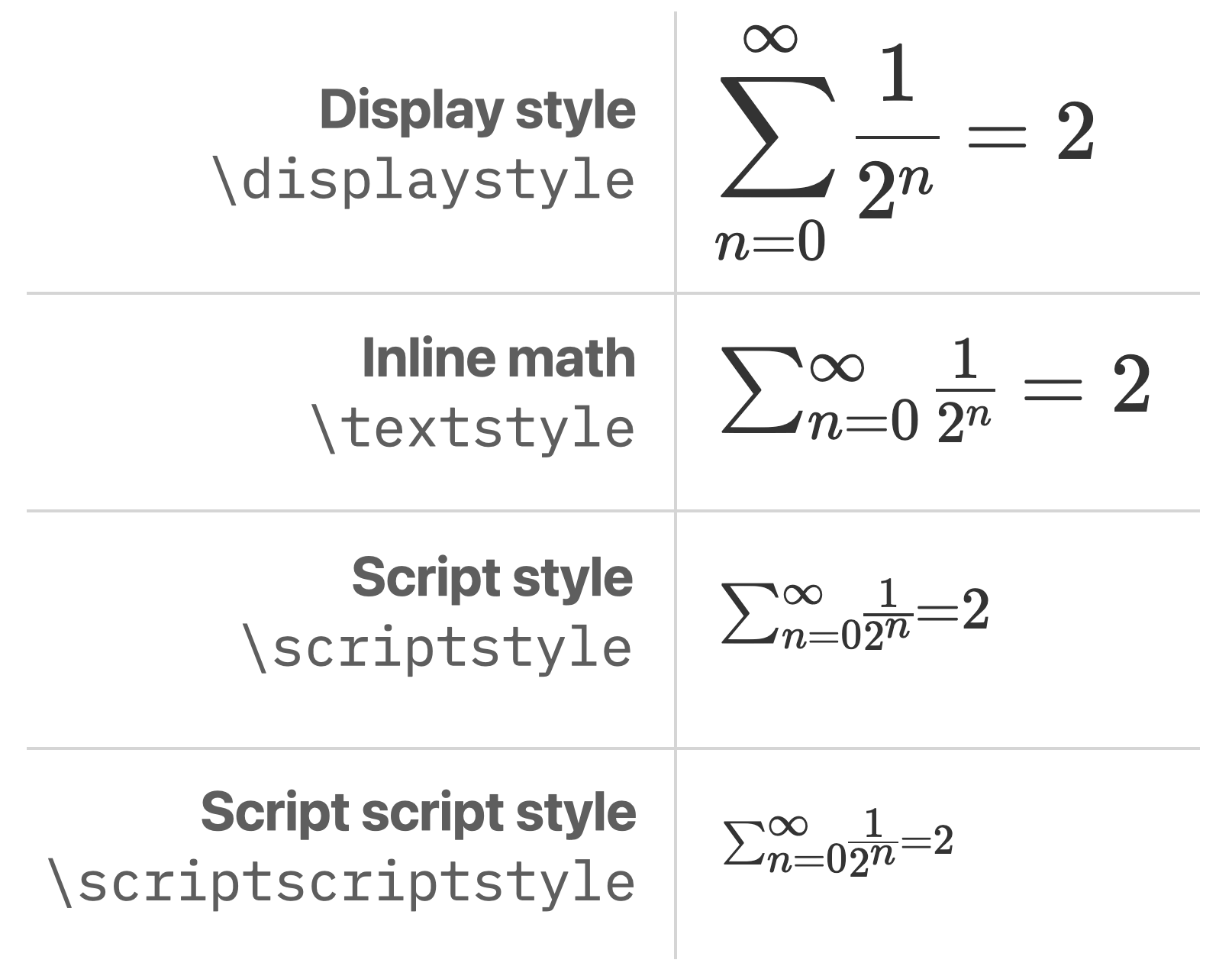
The displaystyle style is most appropriate when there is plenty of space around
the formula. Limits over large operators, such as \sum are displayed above
and below the operator. There is a generous amount of space below the numerator
and above the denominator of fractions, and around relational (=) and binary
(+) operators.
The textstyle style is useful when space is constrained or when displaying
a formula with some regular text around it. The limits of large operators
are displayed after the operator. The numerator and denominator of fractions is
displayed using a smaller font size. However, the font-size for other characters
is not affected.
The scriptstyle and scriptscriptstyle are rarely needed explicitly. The
content is laid out using a smaller font-size (70% and 50% of the base font-size,
respectively) and the spacing between operators is minimized. Note however
that these styles are used automatically in some situations. For example,
when using the displaystyle or textstyle, the limits of a large operator
or the superscript or subscript of a symbol are displayed using these styles.
Notice for example that n=0 in displaystyle does not include space around
the = sign because the limit is displayed in scriptstyle.
To set the default mathstyle of a mathfield, set the mf.defaultMode
property or the default-mode attribute.
Set it to "inline-math" to use textstyle or "math" to use displaystyle.
By default, the mathfield element is laid out on the page as an inline element
when in an inline context (when inside a <p> tag for example).
To get it laid out as a block element, set display: block on the mathfield.
Letter Shape Style
To control which letters are automatically italicized, set the letterShapeStyle property or letter-shape-style attribute.
letterShapeStyle | xyz | ABC | αβɣ | ΓΔΘ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
iso | xyz | ABC | αβɣ | ΓΔΘ |
tex | xyz | ABC | αβɣ | ΓΔΘ |
french | xyz | ABC | αβɣ | ΓΔΘ |
upright | xyz | ABC | αβɣ | ΓΔΘ |
In the ISO style, lower and uppercase roman letter and lower and upper case greek letters are italicized when used as a variable. Mathematical constants such as \(e\) are written upright.
TeX has traditionally implemented a layout option that italicizes romman letters and lowercase greek letters, but not uppercase greek letters.
The French typographical convention is to only italicize lowercase roman letters.
The default letter shape style is auto: if the system locale is "french",
the french style is used, otherwise tex is used.
Editing Options
The editing behavior of a mathfield can be customized by setting some
properties on the mathfield, or the equivalent attributes on the
<math-field> tag.
defaultMode:"inline-math": use inline math mode"math": use the display math mode"text": use the text mode |
removeExtraneousParentheses: automatically remove extra parentheses around a numerator or denominatorscriptDepth: maximum levels of subscript or superscript. Set it to 0 to prevent the input of superscript and subscriptssmartFence: automatically convert parentheses to\left...\rightmarkup.smartMode: switch to text mode when text input is detected, for example when typing "if x > 0"smartSuperscript: automatically move out of a superscript when a digit is typed
These properties can also be passed as an argument to new MathfieldElement() when programmatically creating mathfield elements.
In the interactive code playground below, try some of these options. For example,
in line 1 add the attribute smart-mode=false, then type some parentheses
in the mathfield.
:::html
<math-field smart-mode>
x=\frac{-b\pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}
</math-field>
Handling the Space Bar
In traditional math typesetting, spaces have no effect: the spacing of elements in a formula is determined by the nature of the elements: numbers, punctuation, relational, binary or unary operators, etc...
To control spacing in a formula, use some of the LaTeX spacing commands: \quad,
\qquad, \!, \, (thin space), \: (medium space), \; (thick space), \enskip or \enspace.
By default, pressing the spacebar when in math mode does not insert anything.
To insert a LaTeX command when the spacebar is pressed, set the value of the
mathModeSpace property to that command:
mf.mathModeSpace = '\\:';
Turning off the LaTeX mode
Pressing the \ (backslash) or ESC key switches to the LaTeX mode where it is possible to enter raw LaTeX command. For users familiar with LaTeX, it is a powerful way to enter or edit LaTeX in an expression. However, users unfamiliar with LaTeX may be confused if they accidentally press those keys.
To prevent the LaTeX mode from being enabled intercept the trigger keys and call `preventDefault().
mf.addEventListener(
'keydown',
(ev) => {
if (ev.key === '\\') {
ev.preventDefault();
mf.executeCommand(['insert', '\\backslash']);
} else if (ev.key === 'Escape') ev.preventDefault();
},
{ capture: true }
);
Localization
The user interface of the mathfield is provided in english, arabic, german, greek, spanish, farsi, french, italian, japanese, polish and russian.
The language to use is detected automatically, but it can be overridden by
using the MathfieldElement.locale static property. Setting this property
will affect all mathfield elements on the page.
Decimal Marker
The world is
about evenly split
between using a dot . or a comma , as a decimal marker.
To change the marker used with decimal numbers set the
MathfieldElement.decimalSeparator property to "," or ".".
When set to ",", pressing the , key on a physical keyboard will insert a
{,} LaTeX string, if in math mode and if before a digit.
The LaTeX sequence {,} is traditionally used to correctly typeset the comma
and ensure the correct amount of space around it. Without the {}, the ,
is interpreted as a delimiter and has excessive amount of space around it.
When set to ",", the virtual keyboard is also changed so that the .
keycap is labeled , instead and contextually inserts a {,} when appropriate.
Fraction Navigation Order
When using the arrow keys on the keyboard to navigate a fraction, the order in which the numerator and navigator are traversed can be customized.
To change the keyboard navigation order of fractions set the
MathfieldElement.fractionNavigationOrder property.
The possible values are:
"numerator-denominator": first the elements in the numerator, then the elements in the denominator. This is the default behavior."denominator-numerator": first the elements in the denominator, then the elements in the numerator. In some East-Asian cultures, fractions are read and written denominator first (fēnzhī). With this option the keyboard navigation follows this convention.
Sounds and Haptic Feedback
The mathfield provides some audio feedback when a key is pressed on the virtual keyboard or when an action cannot be performed, for example when trying to delete when the mathfield is empty (the "plonk" sound).
The files for the sounds played by the mathfield should be located in a
directory named sounds next to the mathfield library. If your bundler or
asset management system require a different configuration you can specify
where the sounds can be located using the MathfieldElement.soundsDirectory
property.
MathfieldElement.soundsDirectory =
"https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mathlive/sounds/";
Specific sounds can be disabeld or customized with the MathfieldElement.keypressSound
property.
MathfieldElement.keypressSound = {
spacebar: null,
return: "./sounds/return.mp3",
delete: null,
default: null,
}
Playing "Plonk" Sound
To play the "plonk" sound when an action cannot be performed, use MathfieldElement.playSound('plonk').
MathfieldElement.playSound('plonk');
Disabling Sounds
To turn off the sounds set the MathfieldElement.soundsDirectory property to null.
MathfieldElement.soundsDirectory = null;
Haptic Feedback
When a key on the virtual keyboard is pressed, a small vibration is triggered
on devices that support it. This can be turned off by setting the
MathfieldElement.keypressVibration property to false.
MathfieldElement.keypressVibration = false;
Fonts
The content of the mathfield is displayed using a family of high-quality fonts based on the original Computer Modern font from TeX. The mathfield will not display correctly using another font.
By default, the directory containing the fonts is located next to the file
containing the mathlive library. If your bundler or asset management system
require a different configuration you can specify where the fonts can be
located using the MathfieldElement.fontsDirectory
property.